Hop-Mix-DNS: Hop-wise Mixing Dynamic Negative Sampling for Graph Neural Network-based Recommendation Systems
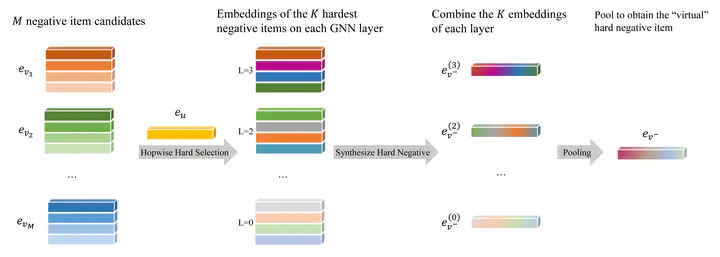 Overview of Hop-Mix-DNS
Overview of Hop-Mix-DNSAbstract
Recommendation system models users’ preference on items based on past interactions history. Lately, the graph neural network (GNN) has become a powerful collaborative filtering (CF) solution, which leverages the high-order connectivity information in the user-item bipartite graph. In training the GNN-based CF models, negative sampling plays an essential role in boosting the model’s performance and improving the training efficiency. However, there has been very limited literature on negative sampling for GNN-based CF. In this paper, we propose the Hop-Mix-DNS method, a novel negative sampling strategy for GNN-based recommenders. It first picks multiple hard negatives on each GNN layer then aggregates them with carefully designed coefficients to synthesize one ‘‘virtual’’ negative item. The advantages are twofold: 1) the model is trained more efficiently as several hard items are included in negative sampling so that there is a larger gradient, 2) it helps to improve the performance because the level of difficulty among negative items is more balanced for training the model. Empirical results on three real-world datasets demonstrate that the Hop-Mix-DNS consistently improves the state-of-the-art GNN-based CF model, LightGCN, by 27% in terms of NDCG@20. Training time is reduced by up to 60% compared to state-of-the-art negative sampling method.